General Arbitration Program
MCLA delivers a highly structured and impartial arbitration program designed to provide binding, enforceable resolutions with the highest level of professionalism and efficiency.
Our Arbitration Program
MCLA offers a comprehensive arbitration program designed to provide parties with a fair, neutral, and efficient process.
Ready to Submit an Arbitration Case?
Important: At this time, submissions cannot be made through our online form.
Please email us directly at info@mediationla.org to initiate your arbitration process or to request assistance.
Why Choose Arbitration?
- Efficiency – Avoid lengthy court delays and resolve disputes faster.
- Confidentiality – Keep your matter private rather than on the public record.
- Flexibility – The process can be tailored to fit the needs of the parties involved.
- Expertise – Arbitrators are highly skilled professionals with experience in relevant areas of law and industry.
What Is Arbitration?
The arbitrator is a neutral expert selected for their knowledge and experience related to the dispute they will decide.
“Arbitration provides a binding decision after a hearing conducted according to agreed-upon rules.”
Testimony presented in arbitration is often less formal than in court, and there is no concern about confusing a jury since the arbitrator alone evaluates the facts and evidence.
“Arbitration awards are binding and can be entered as a judgment in court, carrying the same effect as a judge’s ruling or jury verdict.”
While most arbitration awards cannot be appealed, parties may ask the court to set aside or “vacate” an award under limited circumstances.
The authority of the arbitrator is determined by the parties’ agreement (in the C.A.R. form) and the applicable arbitration rules (see Standard Arbitration Rules below). This gives parties more control over how the process is conducted compared to a traditional courtroom, including decisions about evidence and procedure.
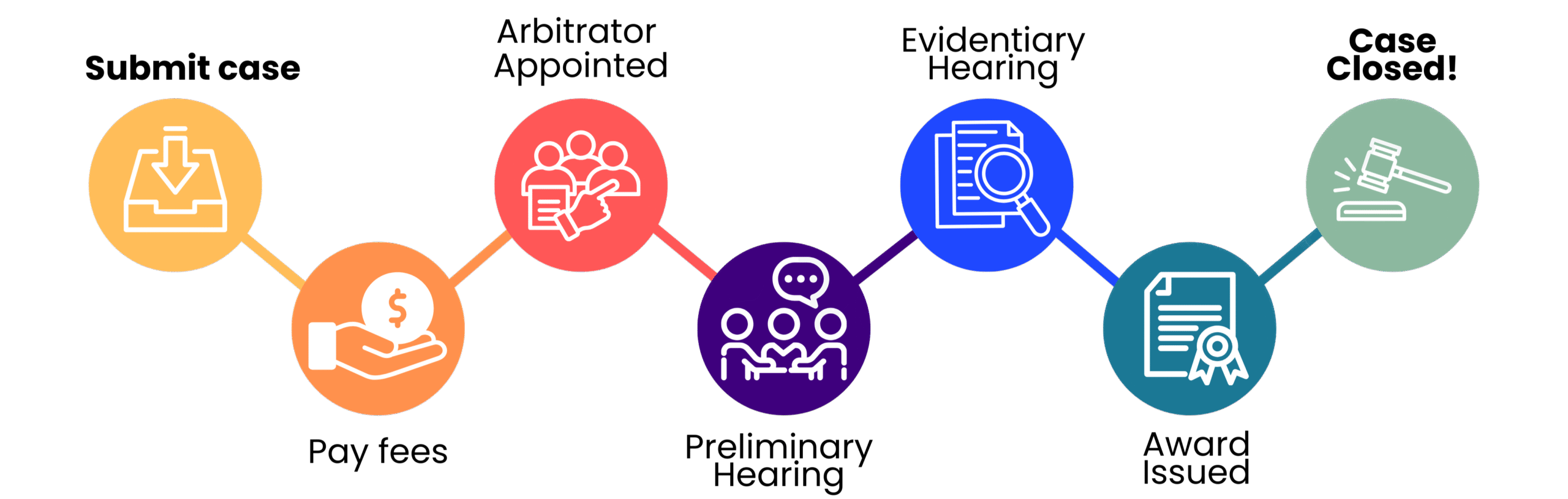
What to Expect in Arbitration
1. Submit Case – The claimant files the case and serves the other party, providing proof. The respondent has 14 calendar days to respond, and the claimant has 7 calendar days to reply to any cross-claims.
2. Pay Fees – Both parties pay the filing fee before the case can move forward.
3. Arbitrator Assigned – An arbitrator is appointed. Any objections to the arbitrator must be filed within 14 calendar days of the response deadline. Both sides exchange documents they will use within 30 calendar days before the preliminary hearing.
4. Preliminary Hearing – Witness lists, exhibits and pre-hearing briefs are due 14 calendar days before the hearing. If a party wants the hearing transcribed, they must arrange this and notify everyone 7 calendar days before the hearing.
5. Evidentiary Hearing – Both parties present their case. Hearings are usually no longer than one day.
6. Award Issued – If post-hearing filings are needed, the case closes within 7 calendar days after the last submission. The arbitrator then issues the award within 30 calendar days after the case closes.
7. Case Closed – The final award, including any fees, is issued within 30 calendar days after the last filing. The award is binding and enforceable.

